Friday December 1 CSL Meeting
Nov 30, 2017 - CSL

Ellen Bartow-Gillies
Penultimate Glacial-Interglacial Climate Variability in the Southern Great Plains of North America
Presenter: Ellen Bartow-Gillies
Time: Friday, 1 December 2017, 2:00-3:00 p.m.
Location: 805 O&M
Abstract: Projections of changes in rainfall under future warming scenarios vary in their sign and intensity over the Southern Great Plains (SGP). A scarcity of local paleoclimate information before the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM) limits our understanding of regional climate responses to changes in mean state and forcing. Here, we present absolutely U/Th-dated oxygen and carbon isotope records from a calcite stalagmite near Georgetown, Texas (30°N, 98°W), spanning 98 to 209 kyr before present (kyr BP). SGP moisture is primarily sourced from the Gulf of Mexico, and precipitation exhibits clear seasonality, with a biannual rainy season divided into late boreal spring and fall. We interpret the oxygen isotopic composition of the stalagmite to reflect changes in rainwater δ18O composition, as well as cave temperature, through time. There are no clear kinetic isotope effects observed within the stalagmite. More negative (positive) δ18O values are a reflection of warmer and wetter (cooler and drier) conditions based on modern observations of rainwater δ18O at the study site. Variations in stalagmite δ13C may be driven by shifts in overlying vegetation type and changes in the rates of karst flow and prior calcite precipitation. The stalagmite records include Marine Isotope Stage (MIS) 5e, an interval where global temperatures may have been as much as 2°C warmer and sea level 4-6 m higher than present. Thus, our δ18O record provides context of unique importance for how SGP hydroclimate may respond to future warming. Prominent features in the δ18O record, including a warm and wet MIS 5e appear to be paced by precession, with the timing of δ18O minima (maxima) broadly consistent with that of maxima (minima) in monthly insolation at 30°N. The δ13C record exhibits a striking similarity to canonical, sawtooth records of glacial-interglacial variability, which suggests Great Plains vegetation communities may be sensitive to the status of Northern Hemisphere glaciation. Our SGP stalagmite records help to reveal the fundamental character of SGP climate response to glacial-interglacial forcings and provide evidence for increased precipitation under past warming conditions.
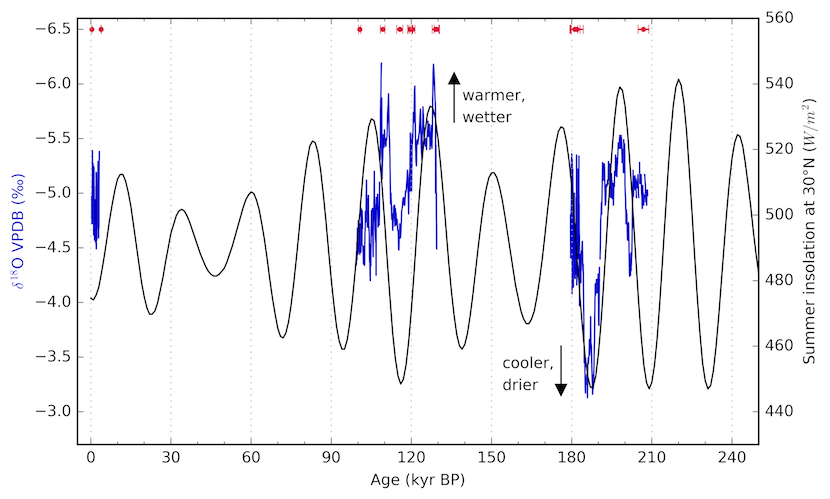 Texas stalagmite δ18O (blue) and summer insolation at 30°N (black) versus time. 14 U-series dates and errors are shown in red. Variations in stalagmite δ18O likely reflect changes in the amount of rainfall in the Southern Great Plains.
Texas stalagmite δ18O (blue) and summer insolation at 30°N (black) versus time. 14 U-series dates and errors are shown in red. Variations in stalagmite δ18O likely reflect changes in the amount of rainfall in the Southern Great Plains.